
Which workpieces are suitable for fixing and machining using CNC porous vacuum chucks? Here are my thoughts based on industry experience.
Most workpieces can be handled using vises and permanent magnetic chucks. However, for some ultra-thin, non-magnetic workpieces, we need to use vacuum chucks to secure them.
Whether it’s a sealing strip vacuum chuck or a porous vacuum chuck, they are all designed to handle thin plate workpieces. The sealing cord vacuum chuck is not suitable for irregularly shaped workpieces and cannot handle workpieces that need to be milled through. The porous vacuum chuck does not have these limitations.
Today, we will mainly discuss the characteristics of CNC porous vacuum chucks and the types of workpieces they are suitable for.
CNC Porous vacuum chucks generally have the following requirements for the appearance characteristics of the workpiece:
- The workpiece needs to have good flatness, generally better than 3.2 micrometers.
- The workpiece needs to have high parallelism, generally better than 0.2 mm.
- The effective coverage area of the workpiece must reach a certain value. For blind plate workpieces, the area of the workpiece is generally required to be more than 60 square centimeters.
- The hollow ratio of the workpiece should not be too high, otherwise, the number of suction holes covered by the workpiece will be insufficient. Generally, it is required that 25 suction holes are covered and functioning to meet the requirements of most CNC machining operations.
- The workpiece should not deform or curl during the machining process; otherwise, it is easy for the workpiece to fall off during machining.
- The thickness of the workpiece should not be too thick, generally within 40 mm.
- The size of the workpiece needs to be comprehensively considered with the diameter and number of suction holes. These are the requirements for the appearance size and characteristics of workpieces when using CNC porous vacuum chucks. Next, let’s introduce the requirements for the material of the workpieces.
Porous vacuum chucks do not have special requirements for the material due to their reliance on the pressure difference formed by air:
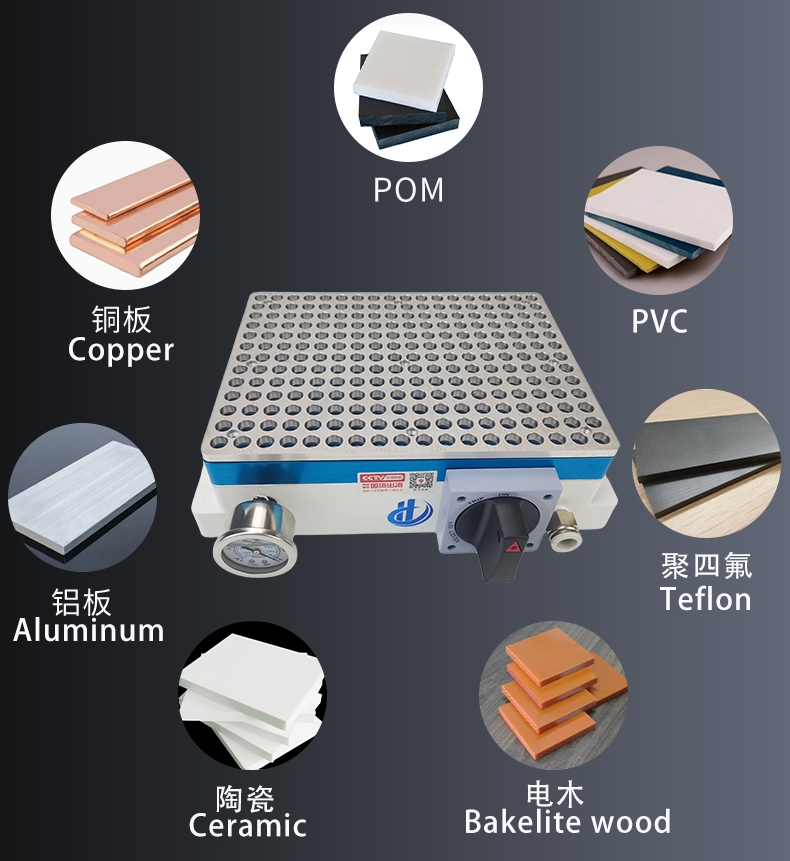
- They can be used regardless of whether the material is magnetic or non-magnetic.
- Ferrous metal materials, such as steel plates.
- Non-ferrous metal materials, such as stainless steel, aluminum alloy, copper, and titanium alloy.
- Non-metallic materials, such as ceramics, quartz, glass, glass fiber, and graphite.
- Polymer materials, such as PTFE, acrylic, POM.
- Wood materials, such as high-quality wood used in engraving machines.
On which CNC equipment can CNC porous vacuum chucks be used?

- CNC three-axis machining centers, which is the most common application.
- CNC four-axis machining centers, which require connecting the chuck to a swivel joint, allowing the worktable to rotate.
- Rectangular grinders, typically used for grinding non-magnetic thin plate workpieces. The size of the workpiece is usually small, so the porous vacuum chuck needs smaller and denser suction holes to ensure that small workpieces can cover more than 25 suction holes.
- Rotary table grinders, which require custom adaptation from the rotary table grinder manufacturer. This requires reserving space for the swivel joint and air pipes at the center of the rotating worktable.
- Large engraving and milling machines, and machining centers used for machining curved workpieces, such as the outer shell of the body. This requires using modular porous vacuum chucks to fix larger cambered surfaces, typically using a single row of holes design. The length of the chuck is generally between 20-50 cm, used with large fixtures to complete the task.
- Small engraving machines, such as those used for processing wooden crafts or the necks of violins and cellos.
What precautions should be taken when using CNC porous vacuum chucks?
- Consider the requirements of the chuck for the flatness and parallelism of the workpiece.
- During machining, coolant (if needed) may gradually enter the chuck. It is necessary to discharge the coolant in real time.
- The vacuum chuck needs to provide a stable negative pressure, and the air pressure and pumping volume should not fluctuate significantly. Otherwise, the suction may weaken at certain moments. It is generally required to install a buffer tank of more than 40 liters between the vacuum system and the vacuum chuck to stabilize the pressure and pumping rate.
- Chips generated by milling and grinding should not clog the suction holes. If a porous vacuum chuck frequently has clogged suction holes, it indicates that the manufacturer’s product is not mature. SOVAC’s CNC porous vacuum chucks can guarantee that even in the presence of a large amount of powdery debris, the suction holes will not be clogged.
- The coolant used can be water-based or oil-based, but it cannot be strongly acidic or alkaline as these liquids are highly corrosive to porous vacuum chucks.
In conclusion, CNC engineers need to gradually deepen their understanding of porous vacuum chucks to fully grasp their advantages and how to mitigate their drawbacks.
#cnc #cncmachining #cncmachine #cncmachinist #grindingmachine #VMC #vacuumplate #vacuumfixture #vacuumclamp #vacuumworkholding #vacuumchuck #vacuumtable #workholding #grindingchinine


adipisci dolores aperiam qui placeat nesciunt soluta vitae fugit veritatis voluptatem odio. porro cum voluptatem dolore incidunt adipisci molestiae nisi. ratione ullam commodi eligendi repellendus omn
sed et architecto sed ratione earum et quia iste illo fugiat qui tempore. et iusto commodi optio minus quia aspernatur.
voluptas saepe laudantium molestiae sit laborum omnis dolorem accusantium qui omnis rerum exercitationem et beatae. quidem ipsum perspiciatis laudantium iure omnis voluptatem recusandae tenetur quia c